reading-notes
Linked Lists
Big O: Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency
Big O notation - apparently, the ‘O’ in big O stands for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.
Big O is used to classify algorithms by their run time or space requirements.
Running time - (time complexity) How long does this function need to complete its task?
Memory Space - (space complexity) How much computer memory resources will this function use to store data and computer instructions? “How efficient is our space consumption?”
Big O’s purpose is to describe a function’s worst case scenario.
Here are the 4 Keys Areas to consider when thinking of Big O:
- Input Size
- Units of Measurement
- Orders of Growth
- Best Case, Worst Case, Average Case
n Input Size: The size of the parameters read by the function.
Units of Measurement - quantify with:
- time in milliseconds (more useful checking the performance on specific hardware)
- number of operations (number of lines of code fun from start to finish)
- number of basic operations (usually the innermost loop)
Memory Space - four sources of memory usage:
-
the space the lines of code itself takes to run the algorithm
-
the space that the input data needs
-
the space needed to hold the output data
-
the space needed to hold working data during run time (stack space, recursive calls)
Orders of Growth - the order of magnitude that time and space requirements go up by when the size of the Input n increases
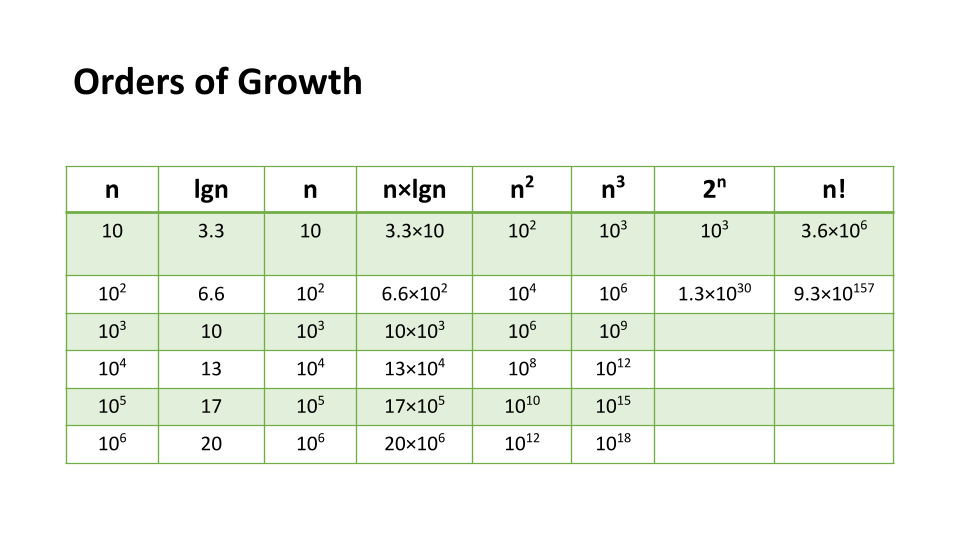
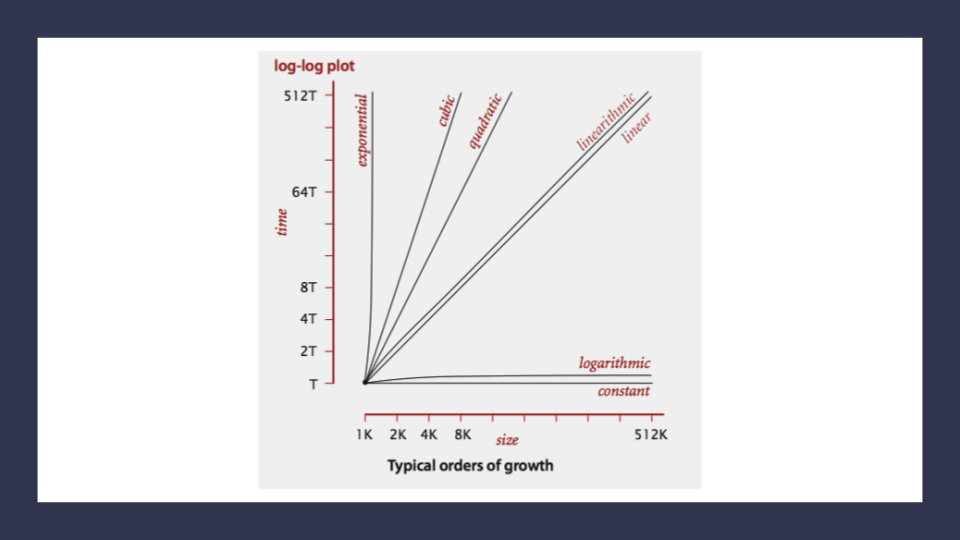
How do we analyze big on with pen and paper?
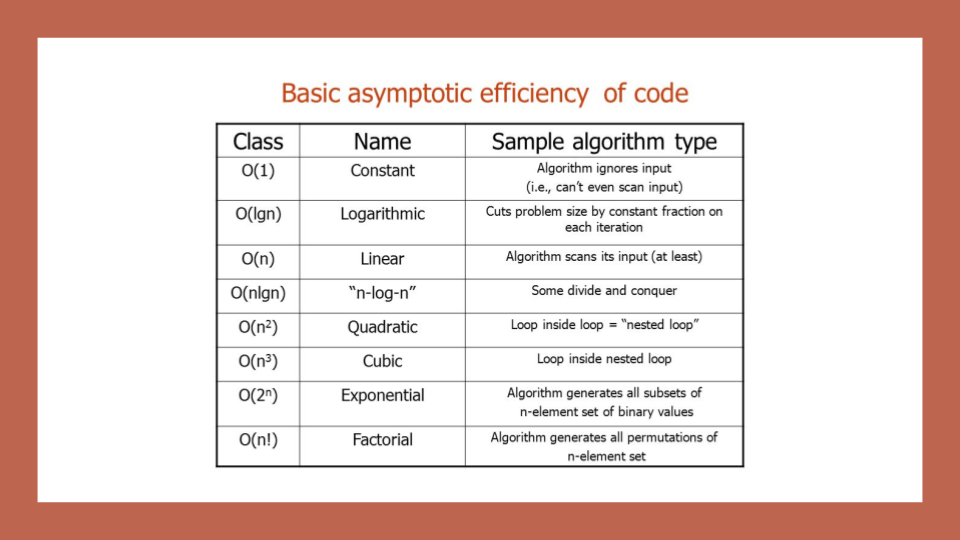
Notes:
- look for nested for loops
- or nested loops, in general
- recursion
- watch a video on simplifying calculating Big O notation for algorithms
- how to explain the notation in plain English